Demat Account
A demat account is a medium which enables people to convert and hold share certificate in electronic mode. A Demat account helps you for document-free trade and transfer transactions.
A Demat account keeps all the shares that you purchase in electronic or dematerialized form. Demat Account works in a similar way to your bank account which holds your money in electronic form, a Demat keep your financial instruments like shares, bonds, government securities, mutual funds, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) in an electronic form.
To buy or Sale shares whether offline or online, it is mandatory to have a Demat account.
How Demat Account works
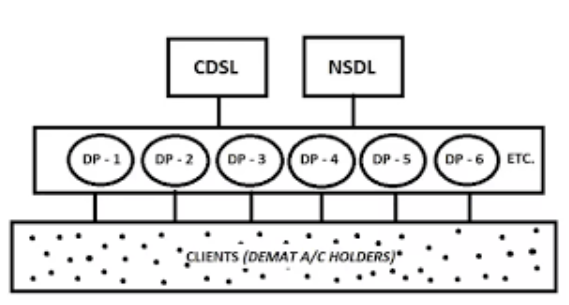
A depository (in simple terms) is an organization holding a pool of pre-verified shares held in electronic mode that offers faster & efficient way of settlement of transactions.
There are two depositories in India – the CDSL and NSDL. They hold all the demat accounts. The central depository works like a bank and keeps details of your shareholding.
A Depository Participant (DP) is an intermediary between the Shareholder and the Central depository organization (CDSL /NSDL). A DP is typically a financial organization like a broker, financial institution, or custodian acting as an agent of the depository to make its services available to the investors.
The Demat account keeps all your securities like Shares, Mutual funds, debentures in electronic form. Just like a bank account you can any time check your account and can see your portfolio holding and its details. These are getting updated automatically every time you carry out a transaction – be is buying or selling a security.
Benefits of Dematerialization
- Reduction of Cost: The depository system helps in reducing the cost of new issues due to lower printing and distribution costs. It increases the efficiency
- The depository system would help in reducing the risks involved in keeping physical certificates with us, e.g., loss, theft, damage, forgery, etc.
- Speed: Due to electronic way of executing the transaction which happens very quickly and reduces delay in registration of shares.
- Very Simple and convenient way to hold securities
- Immediate transfer of securities
- No stamp duty on transfer of securities
- No paperwork for transfer of securities
- Lower transaction cost
- No need of lot wise transfer of securities, even one share can be sold or held.
- Automatic transfer into demat account for shares arising out of bonus/split, consolidation/merger, etc.
- No need to have separate demat account for equity and debt instrument , one demat can hold both equity and debt instruments.
- Investor can trade in securities from anywhere (e.g. even from home).
How to Open a Demat Account?
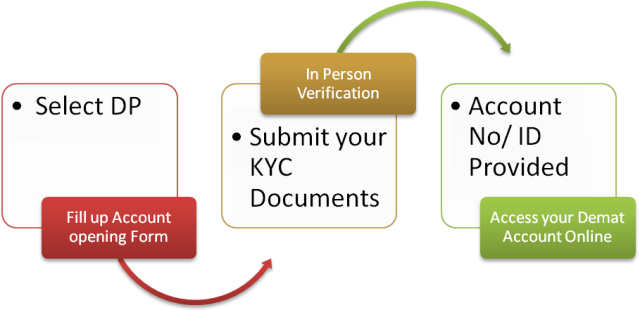
1. Select a Depository Participant (DP): The first step is to select a Depository Participant (DP) you would like to open your account with, this institution will serve as the intermediary between you and the depository. DPs can be banks, brokers, or online investment platforms.
2. Submit your KYC Documents: Submit the form is given to you for opening an account, the KYC form, passport size photographs, your PAN card (Permanent Account Number), and other photocopied documents.
At this point, you will be given the option to name a person as your nominee. They will be assigned with the responsibility of your shares if something were to happen to you. The choice of one's nominee can be changed, if need be in the future, by refilling the same form.
The KYC form also has the agreement between Depository Participant & Investor which comprises the terms of agreement, rules, and regulations, and charges you will incur whilst holding a Demat account. This form also includes the rights of the investor and duties of the DP.
3. Appear for In-Person Verification: An In-Person Verification may be carried out by a person from your DP's firm to ensure that the details provided by you in the form are authentic.
4. Get Beneficiary Owner Identity (BOID): Once your application has been processed and your DP has facilitated the opening of your account, he/she will give you a Beneficiary Owner Identity (BOID) - a unique account number - that you can use during future transactions and access your account.
You need to open a trading account along with the Demat account so that you can immediately begin buying and selling shares.
Documents Needed to Open a Demat Account
The documents can be categorized into two parts for opening a Demat account one is a proof of address and another one is proof of identity. In addition, applicants will also need to submit a copy of their PAN card and passport-sized photographs.
Proof of Identity for opening a Demat account:- Voter's identity card
- Income tax returns
- Bank attestation
- Electricity bill
- Identity cards issued by the central or state government along with a photograph
- Identity cards issued by professional bodies like the Bar Council, Institute of Chartered Accountants of India, and Institute of Cost Accountants of India
- Passport
- Driving license
- PAN card
- Identity cards issued by public sector undertakings, regulatory or scheduled authorities, public financial institutions, university-affiliated colleges, or scheduled commercial banks
- Identity cards issued by public sector undertakings, regulatory or scheduled authorities, public financial institutions, university-affiliated colleges, or scheduled commercial banks
- Voter's identity card
- Self-declaration by Supreme or High Courts judges
- Agreement for sale
- Leave and license agreement
- Verified copies of electricity bill
- Bank statement or passbook
- Driving License
- Residential telephone bill
- Ration card
- Identity cards issued by professional bodies like the Bar Council, Institute of Chartered Accountants of India, and Institute of Cost Accountants of India
- Passport
Demat Charges:
There are four kinds of major charges normally levied on a Demat account: Account opening fee, annual maintenance fee, custodian fee, and transaction fee. Amount charges for all fees would vary from DP to DP.
Account-opening feeThis is charged for administrative expenses incurred on the opening of Demat account, many brokers waive account opening fees to promote their services.
Annual maintenance feeThese expenses are recurring in nature and charged annually, this is also known as folio maintenance charges, and is generally levied in advance.
Transaction feeThese fees charged mainly on monthly basis on all the transactions of buying /selling of securities to and from the account. The charges would depend on DP to Dp, some DPs, such as SBI, charge a flat fee per transaction, HDFC Bank and ICICI Bank pay the fee to the transaction value, which is subject to a minimum amount. The fee also differs based on the kind of transaction (buying or selling). Some DPs charge only for debiting the securities, while others charge for both. In addition, service tax is also charged by the DPs.
In addition to the other charges, the DP also charges a fee for converting the shares from the physical to the electronic form or vice versa. These charges may vary for both Demat (physical-to-electronic) and remat (electronic-to-physical) requests.
- Transfer of Shares between (depository participant) DPs:
To transfer shares, an investor has to fill one of two kinds of Depository Instruction Slip (DIS). For example::
ü If there is one Demat account with CDSL and the other Demat account with NSDL, then an Inter-DIS is needed.
ü Now that the correct DIS has been determined, information pertaining to the transfer transaction has to be entered: scrip name, INE number, quantity in words and figures.
ü Finally, the investor should submit that DIS to the broker with signatures. signatures.
ü The transfer broker shall accept that DIS in duplicate and acknowledge receipt of DIS on a duplicate copy.
The investor should submit the DIS when the market is open. Accordingly, the date of submission of DIS and the date of execution of DIS can be the same or a difference of one day is also acceptable. The investor also has to pay the broker some charges for the transfer.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
1. How to operate my online Demat account?
To operate the online Demat account, one must have to apply for it and should get the client ID and password. He can access his account with these details. If Investor wants to buy any share he should raise order via trading account linked to Demat account, the broker would credit the purchased share in his Demat account and he wishes to sell the same he can sell the same via his trading account. Once the order is processed, the shares will be debited from the account and he would get the amount credited in his account.
-
2. What if I already have a Demat account with another depository?
You can change your Demat account from one depository to another by filling the Delivery Instruction Slip (DIS) book and submit it to your broker. You need to fill the relevant details like your securities information, ISIN number, and the new depository participant's ID, etc. Your broker will then send your request to the DP. The DP will then transfer the shares to your new Demat account. If everything works well then the transfer takes place within 24 hours or the next business day. Brokers charge a cost for the transfer of a Demat account which would differ from broker to broker.
-
3. Is it necessary to have a bank account to create a Demat account?
Yes, it is compulsory. Without a bank account, you are not able to open it.
-
4. What is the difference between trading and demat account?
Yes. A trading account is used to place buy or sell orders in the stock market. The Demat account is used as a bank where shares bought are deposited in, and where shares sold are taken from.
-
5. Is it necessary to have a demat account for SIP?
Demat Account is mandatory for trading in the stock market. It is not required for Mutual Fund investments of any kind including SIP. For Mutual Funds, the mandatory requirement is filling up a Know Your Customer or KYC.
-
6. Is demat account necessary for trading?
To invest in the stock market and buy equity, you need three things. First, a bank account, second trading account to place the order of buying & selling, third a Demat account to hold your securities in electronic form.
-
7. What is the meaning of trading profit and loss account?
Trading profit and loss account. an account which details the gross profit or loss made by an organization for a given period trading account, and after adding other income and deducting various expenses, is able to show the profit or loss of the business.



0 Comments